Myasthenia Gravis is a rare but impactful condition that affects the nervous system and muscles, causing significant muscle weakness. Although it can affect a wide range of people, including children and adults, myasthenia gravis is more common among women under 40 and men over 60.
This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of this complex condition.
CONTENT:
- Causes of Myasthenia Gravis
- Myasthenia gravis symptoms
- Diagnosis and Evaluation
- Treatment of this disease
- Conclusion
Causes of Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis is an autoimmune disease, which means the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues. In the case of myasthenia gravis, the antibodies destroy or block the acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction, interfering with the transmission of nerve signals to the muscles.
-
Autoimmunity – The Erroneous Attack of the Immune System
Myasthenia Gravis is defined as an autoimmune disorder where the immune system, responsible for defending the body against foreign invaders, turns against its own tissues. In the case of myasthenia gravis, this autoimmunity is manifested by the production of antibodies that target acetylcholine receptors.
-
Antibodies and Acetylcholine Receptor Blockade
Antibodies specific to myasthenia gravis bind to acetylcholine receptors located at the neuromuscular junction, the crucial place where nerves and muscles communicate. These receptors are essential for transmitting nerve signals to muscles, coordinating contraction and movement.
-
Interference with the Transmission of Nerve Signals
When antibodies block or destroy acetylcholine receptors, the normal process of transmitting nerve signals is disrupted. This blockage leads to muscle weakness because signals do not reach the muscles efficiently, resulting in poor muscle function.
-
Neuromuscular Junction – Vulnerable Point
The neuromuscular junction is a vulnerable point in the muscular system, and autoimmune attack directed against it has significant consequences. Progressive muscle weakness and variability of symptoms are directly related to the compromise of this essential junction.
-
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Although the exact causes of this disease are not fully understood, there are suggestions that genetic and environmental factors may play a role in triggering the condition. Certain people may have a genetic predisposition to autoimmune disorders, and environmental factors such as infections or exposure to certain substances may contribute to the disease.
-
Thymus and Its Role
The thymus, a gland located in the upper part of the chest, produces white blood cells and plays an important role in the functioning of the immune system. In myasthenia gravis, the thymus can be affected, contributing to the abnormal generation of antibodies.
Myasthenia gravis symptoms
The symptoms of this disease vary and can affect different areas of the body. Some of the more common symptoms include:
-
Variable Muscle Weakness
One of the hallmarks of myasthenia gravis is muscle weakness, which can range from mild fatigue to significant difficulty in performing daily activities. This weakness can affect different muscle groups, including those of the limbs, neck and trunk.
-
Swallowing and Speaking Difficulties
Weakness of the muscles involved in the swallowing process can cause difficulty in consuming food and liquids. This disease can also affect the muscles of speech, causing dysarthria or slurred speech, thus impacting everyday communication.
-
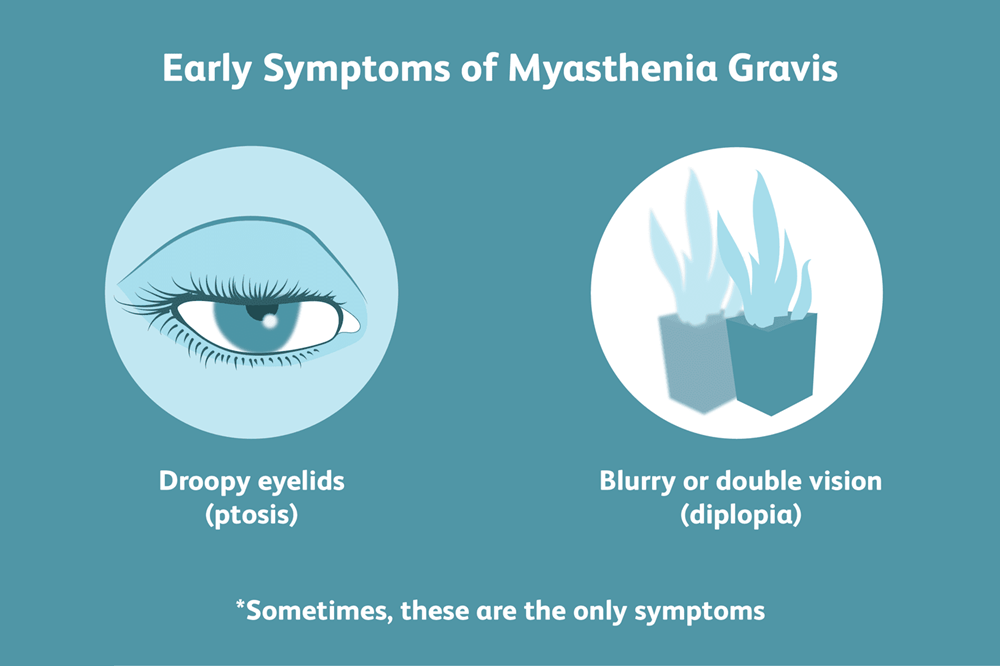
Diplopia (Double Vision)
Diplopia, or double vision, is a common symptom in myasthenia gravis. This usually occurs due to weakness of the muscles responsible for aligning the eyes, which causes distorted vision.
-
Decreased Muscle Strength at the Face Level
It can affect facial expressions, resulting in a stiff or asymmetrical appearance of the face. People with this disease may have difficulty expressing emotions or have difficulty controlling facial muscles.
-
Variability of Symptoms
A notable aspect of this disease is the variability of symptoms. Muscle weakness can fluctuate in intensity throughout the day, being more pronounced during periods of stress or fatigue. This variability often makes diagnosis difficult and requires careful evaluation by a specialist.
-
Difficulty in Lifting Objects or Tilting the Head
Muscle weakness can affect physical abilities, such as lifting objects or holding the head up. These difficulties can affect the patient’s independence and overall quality of life.
Early recognition and appropriate management of these symptoms are essential to improve the quality of life of patients with myasthenia gravis. The integrated approach of a specialized medical team can help stabilize symptoms and optimize treatment.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
The diagnosis of myasthenia gravis involves a careful clinical evaluation, muscle function tests, as well as blood tests to detect the presence of antibodies specific for this disease. Electrical tests, such as electromyography, can provide additional information about muscle and nerve function.
Treatment of this disease
Although there is still no cure for myasthenia gravis, there are treatment options that can relieve symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life. These may include:
- Medication: Medicines that improve communication between nerves and muscles or reduce the activity of the immune system
- Physical Therapy: Adapted exercise can strengthen muscles and improve overall function
- Surgery: In severe or treatment-refractory cases, surgery to correct muscle and nerve problems may be considered.
Conclusion
Myasthenia Gravis presents a complex challenge for those affected, but with proper management, many patients can lead normal lives. Early diagnosis and close collaboration with specialized medical equipment are essential in the management of this condition. As research continues to bring new insights into this disease, the hope for more effective and better tolerated treatments remains at the fore.