Oriental treatments for back pain are a source of growing interest in the modern world of health and wellness. In an age where many are turning to natural and alternative solutions for managing pain and discomfort, traditional methods from the East are becoming more popular and sought after.
From age-old techniques like acupuncture and Tui Na massage, to more recent practices like yoga and Tai Chi, Eastern culture offers a diverse range of treatments that focus on restoring physical and energetic balance in the body.
In this article, we will explore some of the most effective and influential Eastern back treatments and highlight how they can help reduce pain and improve quality of life.
CONTENT:
- The ancient treatment for back pain
- Chinese method of treating pain
- Tai Chi for back pain
- Tui Na massage
- Plants and natural remedies
- Which of the oriental treatments for back pain is the best?
The ancient treatment for back pain
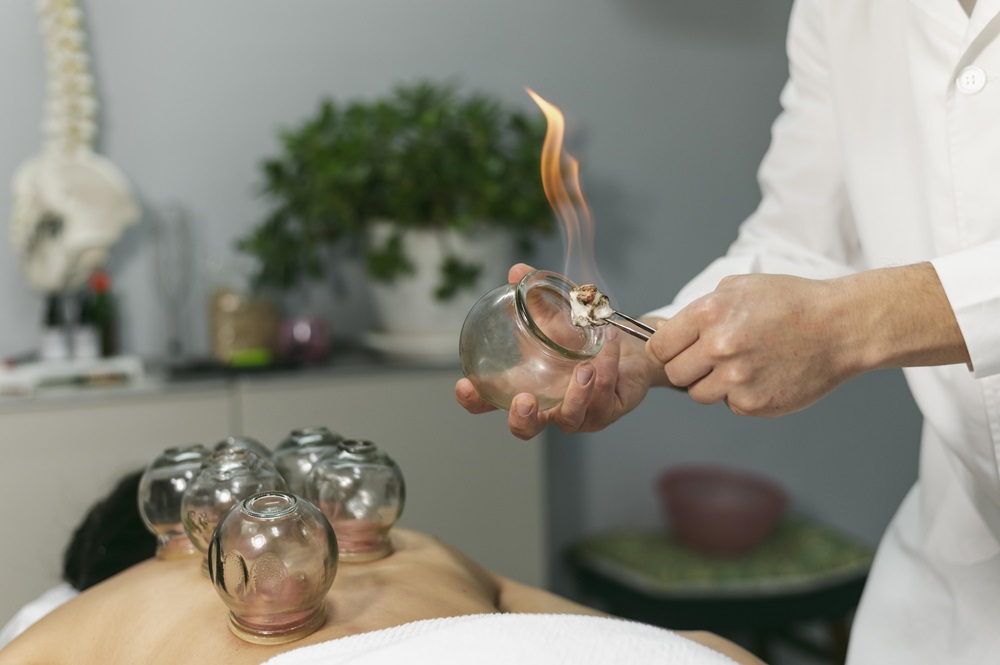
Cupping therapy is one of the oldest and most traditional oriental treatments for back pain. It has ancient origins in the ancient cultures of the Middle East, Asia and Africa. Traditional Chinese, Egyptian, Arabic, and Greek medicine have long recognized the benefits of this therapy in treating various conditions, including back pain.
The basic principle of cupping therapy is to create a vacuum inside special containers, known as cups, and apply them to the skin. This creates suction on the skin and underlying tissues inside the cup, yielding several beneficial effects on the body.
Cupping therapy can reduce pain and discomfort in cases of back pain through several mechanisms:
-
Improve blood circulation
Applying cupping to the skin can stimulate blood flow to the affected area, which helps deliver oxygen and nutrients essential for tissue healing and reducing inflammation.
-
Release muscle tension
Cupping therapy can help relax tight back muscles and reduce muscle spasms that can contribute to back pain.
-
Removal of toxins and congestion factors
Cupping creates negative pressure that can help remove toxins and stagnant fluids from tissues, helping to reduce inflammation and pain.
-
Stimulating Acupuncture Points
In certain cupping therapy methods, cups placed on specific acupuncture points help balance Qi flow, relieving back pain linked to energy imbalances.
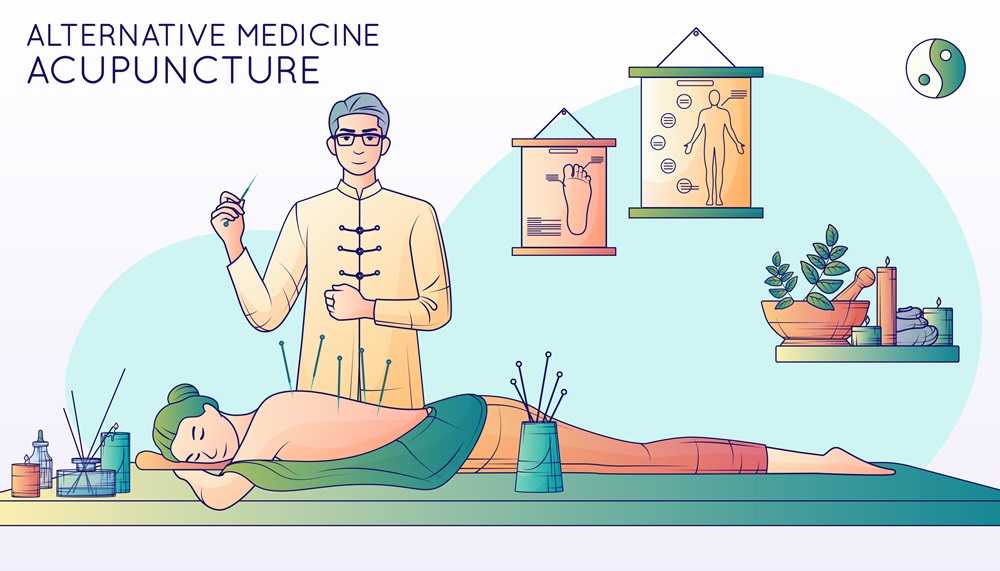
Chinese method of treating pain
One of the most well-known and widely used Chinese methods of pain treatment is acupuncture. Traditional Chinese medicine, with its millennia-long history, regards this practice as one of the most effective pain treatment methods.
Acupuncture is based on the concept that there is a flow of energy or Qi in the body that travels along certain pathways or meridians. When a blockage or imbalance occurs in this energy flow, it can lead to pain or disease. The purpose of acupuncture is to restore energy flow and balance in the body by stimulating specific acupuncture points along the meridians with very fine needles.
By stimulating these acupuncture points, practitioners believe acupuncture can:
- Restores the energy balance in the body.
- It stimulates the release of natural chemicals such as endorphins, which can reduce pain and promote a sense of well-being.
- Improve blood and lymph circulation in the affected area, thus contributing to tissue healing and regeneration.
Acupuncture effectively treats various pains like back pain, headaches, joint and muscle pain, menstrual pain, and more. Over the years, numerous studies have confirmed acupuncture’s effectiveness in reducing pain and improving quality of life.
Tai Chi for back pain
Tai Chi is a traditional Chinese practice that combines slow, fluid and graceful movements, conscious breathing and meditation to promote physical and mental health and well-being. Although known for its benefits in improving balance, flexibility, focus and relaxation, Tai Chi can also be an effective tool in managing back pain.
Here are some ways that practicing Tai Chi can help reduce back pain:
-
Improving Posture
Tai Chi emphasizes maintaining correct and balanced posture during movements. By practicing Tai Chi regularly, you will become aware of your posture and learn to align your spine correctly, which can help reduce tension and pressure on your back.
-
Strengthening the back muscles
The slow and controlled movements of Tai Chi involve strengthening and toning the back muscles, abdomen and other muscle groups that support the spine. This can help increase back stability and strength, reducing the risk of injury and pain.
-
Improve flexibility and mobility
Tai Chi includes a variety of movements that involve stretching and flexibility of the spine, joints and muscles. By practicing Tai Chi, you will improve the flexibility and mobility of your back, which can reduce stiffness and tension and increase your range of motion.
-
Relaxation and stress reduction
Tai Chi promotes relaxation and mental calm through conscious breathing and moving meditation. Reducing stress and mental tension can have a positive impact on back pain, as chronic stress can contribute to increased muscle tension and pain.
To benefit from these effects, it’s recommended to regularly practice Tai Chi, preferably under the supervision of a qualified instructor. It is important to adapt movements to individual abilities and needs and to communicate with your instructor about any health problems or pain you may experience during practice. With patience and consistent practice, Tai Chi can be an effective and enjoyable way to manage and prevent back pain.
Tui Na massage
Tui Na massage is a traditional form of oriental treatment for back pain, practiced for centuries in China. It is also a complex therapeutic technique that involves the use of pressure, frictional movements, tapping and joint manipulations to improve blood circulation, energy balance and internal organ function.
When it comes to back pain, Tui Na massage can be extremely beneficial due to its focused and personalized approach. Here’s how Tui Na massage can help treat back pain:
-
Muscle relaxation
Tui Na massage can help relax tense muscles and reduce stiffness in the back area. By applying pressure and friction movements to the appropriate areas, the therapist can release built-up tension in the muscles and improve blood flow to the affected area.
-
Spinal Alignment
The manipulation techniques used in Tui Na massage can help correct spinal alignment and improve posture. This can reduce pressure on the intervertebral discs and lessen the discomfort associated with back pain.
-
Acupuncture point stimulation
Tui Na massage can also involve stimulating certain acupuncture points along the energy meridians to unblock the flow of Qi and restore energy balance in the body. This can reduce pain and inflammation and promote the body’s natural healing.
-
Improving Blood and Lymphatic Circulation
Tui Na massage stimulates back circulation, aiding toxin elimination and healing.
Consulting a qualified and experienced Tui Na massage therapist ensures proper and safe treatment for back pain.
Plants and natural remedies
Herbs and natural remedies play an important role in traditional oriental medicine. They offer a diverse range of options for treating various conditions, including back pain. These remedies are valued for their effectiveness in reducing pain and inflammation with fewer adverse effects than synthetic drugs.
Among the herbs and natural remedies commonly used for back pain in traditional oriental medicine are:
1. Ginger
Ginger is recognized for its powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Eating ginger can help reduce the inflammation and pain associated with back pain. Ginger can also be applied topically as compresses or oils to soothe inflamed and painful areas.
2. Turmeric
Turmeric contains an active substance called curcumin, which is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Regular consumption of turmeric or curcumin supplements can help reduce the inflammation and pain associated with back pain.
3. Arnica
This herb is known for its use in treating inflammation and muscle and joint pain. Arnica ointments and creams relieve discomfort and reduce inflammation in the affected area of back pain when applied topically.
4. Angelica sinensis (Dang Gui)
This herb is frequently used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat back pain, especially in cases associated with energy and circulatory imbalances. Dang Gui is often used as a decoction or in supplement form to promote blood circulation and reduce pain.

Also, you can use these herbs and natural remedies as dietary supplements, teas, salves, essential oils, or compresses to help manage back pain.
Which of the oriental treatments for back pain is the best?
Determining the best oriental treatments for back pain is challenging due to varying effectiveness influenced by multiple factors. For instance, the cause of the pain, its severity, the individual’s health, and other personal conditions. However, some research and clinical trials suggest that acupuncture may be one of the most effective options for the treatment of back pain.
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body, has been the subject of various studies that have also investigated its effectiveness in treating back pain. Many of these studies have shown that acupuncture can be effective in reducing pain and discomfort associated with back pain, as well as effective in overall back function.
A 2017 review in JAMA Internal Medicine found acupuncture significantly reduces chronic back pain compared to sham or no treatment. Other studies have also suggested that acupuncture may be as effective or even more effective than conventional therapies such as drugs or physiotherapy in managing back pain.
However, treatment effectiveness may vary, and acupuncture may be more suitable for certain types of back pain or individuals.












 Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections
Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections Virtual reality (VR) technology and biofeedback
Virtual reality (VR) technology and biofeedback Therapy through specific exercises
Therapy through specific exercises