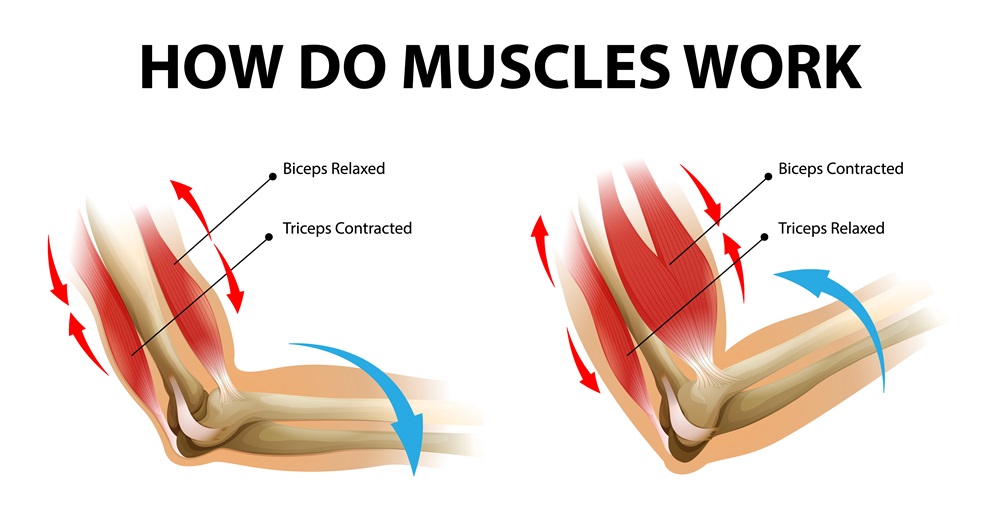
Rhabdomyolysis is a serious medical condition in which skeletal muscles suffer significant damage, releasing harmful substances into the blood.
This condition can have serious health consequences and requires immediate medical attention. In this article, we will explore the causes, risk factors, and treatment options associated with rhabdomyolysis.
CONTENT:
Causes of Rhabdomyolysis
The causes of this condition can vary, and understanding the factors that contribute to its occurrence is essential for the prevention and proper treatment of rhabdomyolysis.
-
Severe Muscle Trauma
Car accidents or other major physical trauma can lead to massive muscle damage. Following such events, muscles can be subjected to stressful physical force, causing them to release myoglobin into the blood and trigger the process of rhabdomyolysis.
-
Intense Exercise
Strenuous physical activities or prolonged training can cause muscle damage. When muscles are overworked or not given the necessary recovery time, they can suffer damage that results in the release of myoglobin into the bloodstream.
-
Metabolic Myopathy
Metabolic disorders, whether genetic or acquired, can contribute to rhabdomyolysis. These conditions affect the way the body produces, uses or stores energy, thereby affecting muscle health.
-
Infections
Some viral or bacterial infections can directly affect the muscles, thus triggering rhabdomyolysis. During an infection, the immune system can react by causing inflammation and destruction of muscle cells, releasing myoglobin into the blood.
Understanding these varied causes is essential for identifying potential risk factors and implementing preventive strategies. Regardless of the cause, early recognition of symptoms and prompt medical intervention can make the difference in effectively managing rhabdomyolysis and avoiding the serious complications associated with this severe muscle condition.
The most common risk factors
In continuing to explore rhabdomyolysis, it is crucial to look at the risk factors that may contribute to the development of this serious muscle condition. The knowledge of these factors becomes essential for the adoption of preventive measures and for the adequate management of the risks associated with the disease.
-
Rapid Development of Exercise
A sudden increase in the intensity or duration of exercise can put excessive strain on the muscles. When they are not prepared for such a change, rhabdomyolysis can be triggered. It is important to take a gradual approach in planning and implementing exercise programs to avoid muscle overload.
-
Dehydration
Inadequate hydration is a significant risk factor for rhabdomyolysis. When water levels in the body are low, muscles can be more susceptible to injury and damage. Ensuring adequate hydration is essential for maintaining muscle health and preventing rhabdomyolysis.
-
Excessive Consumption of Alcohol or Toxic Substances
Toxic substances, including alcohol, can worsen muscle damage and contribute to rhabdomyolysis. These substances can affect normal muscle function, increasing the risk of injury and the release of myoglobin into the blood. Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding toxic substances are essential preventive measures.
-
Hereditary Muscle Diseases
Certain genetic conditions may predispose to rhabdomyolysis. These inherited muscle diseases can affect normal muscle structure and function, increasing the risk of myoglobin damage and release. In these cases, careful monitoring and medical management are necessary to minimize the associated risks.
Finally, identification and awareness of the risk factors associated with rhabdomyolysis play a crucial role in preventing the onset of this serious muscle condition. Adopting a balanced lifestyle that includes safe exercise practices and avoiding risky behaviors is key to protecting muscle health and preventing rhabdomyolysis.
Symptoms of this disease
When discussing rhabdomyolysis, it is essential to also focus on the signs and symptoms that may indicate the presence of this serious muscle condition. Understanding the symptoms is crucial for early identification and prompt intervention, thereby facilitating effective disease management.
1. Severe Muscle Pain
One of the most obvious signs of rhabdomyolysis is the presence of intense muscle pain. They usually manifest in the affected area and can range from discomfort to severe pain. Patients often report a burning or tightening sensation in the muscles.
2. Inflammation and Tenderness
Muscles affected by rhabdomyolysis may become swollen and tender to the touch. Moreover, inflammation is a common reaction to massive muscle damage, and this tenderness can create considerable discomfort.
3. Dark Urine
A classic sign of rhabdomyolysis is a change in the color of the urine. It becomes dark, ranging from brown to dark red. This change indicates the release of myoglobin into the blood, which can put pressure on the kidneys and contribute to kidney failure.
4. Muscle Weakness
Rhabdomyolysis can cause a significant loss of muscle strength and ability to move. Patients may experience general weakness and difficulty in carrying out daily activities.
Treatment methods
The treatment of rhabdomyolysis involves several essential strategies. Rehydration by intravenous fluids is crucial to prevent kidney failure. Furthermore, careful monitoring of renal function and electrolyte levels is essential for effective management of the condition.
Also, identifying and treating the underlying cause, such as infection or trauma, plays an important role in the healing process. It is also recommended to avoid strenuous exercise to allow the muscles to recover.
In conclusion, rhabdomyolysis should not be underestimated, and awareness of symptoms and prompt access to medical care can make a difference in preventing serious complications associated with this severe muscle condition. Adopting a balanced lifestyle that includes moderate exercise practices and adequate hydration can help prevent the risk of developing rhabdomyolysis.