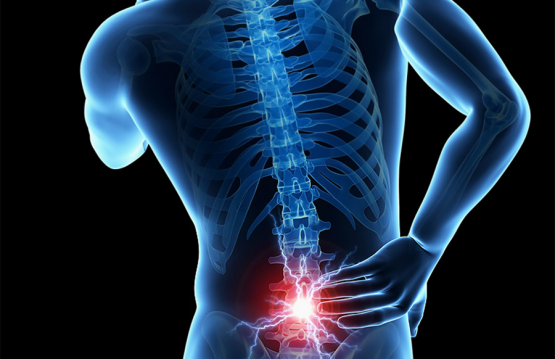
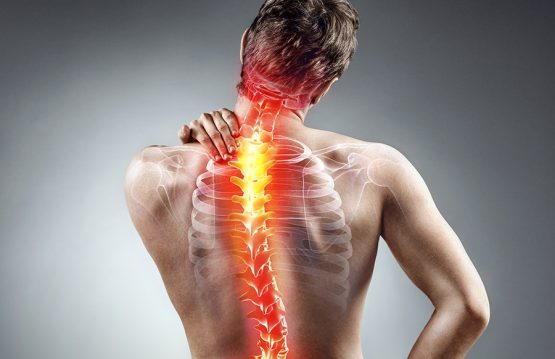
Coccyx pain can be caused by an inflammation located in the coccyx, which is usually associated with local pain and tenderness around the terminal bone portion of the spine called the coccyx, between the buttocks, above the anus. The pain is often exacerbated when an individual is sitting.
Knot pains have their organic headquarters in the coccyx, which is the last segment of the spine.
Due to the terminal and superficial position occupied by it in the structure of the posterior pelvic wall, most of the symptoms are caused by trauma by direct mechanism: falling on the coccyx, kicking in this region or by repeated micro-traumas as in the case of drivers or professionals involves sitting for a long time.
CONTENT:
Causes of coccyx pain
- Disease of the spine affecting the coccyx
- Diseases of the nerves and muscles of the pelvic floor
- Pathological processes in the bones of the pelvis
- Direct or sigmoid diseases (hemorrhoids, proctitis, rectal fissures)
- Perineum omission (for example, due to a difficult birth)
- Perineal trauma during childbirth (hemorrhage in the subcutaneous adipose tissue around the coccyx)
- Intestinal damage, which leads to diarrhea or constipation and therefore the habit of sitting in the toilet for a long time
- Diseases of the genitourinary system
- Coccyx cyst
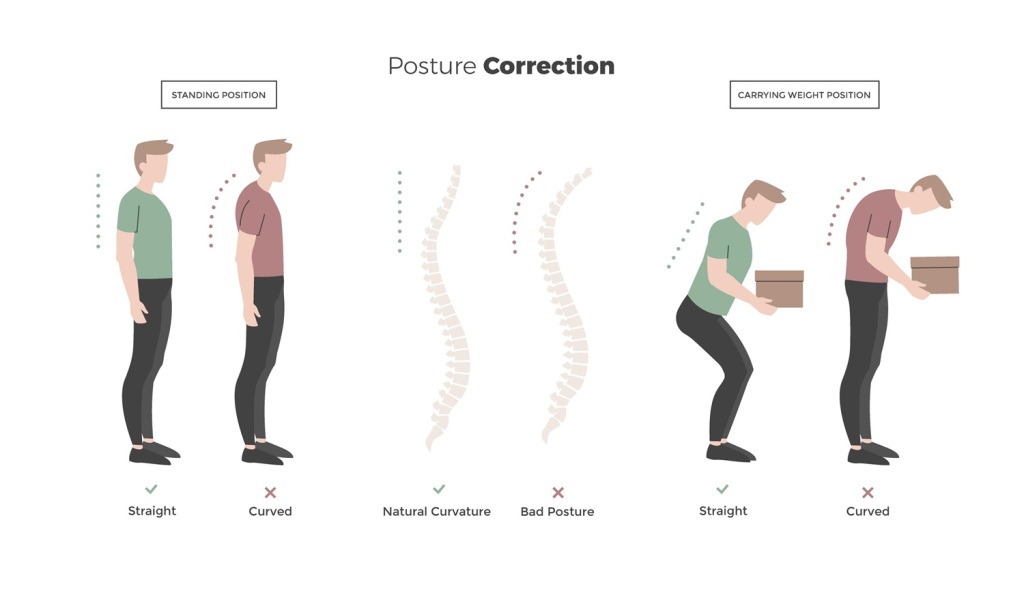
- The habit of constantly sitting on a chair
- Emotional shock, stress or shock
- Tight clothing (jeans), which puts pressure on the coccyx
Usually, pain in the coccyx occurs immediately after injury.
But in some cases, the pain may be mild and pass quickly, but after a few years, it suddenly reappears, with severe pain or burning sensation in the area.
The cause of the pain is usually due to sedentary lifestyle or prolonged sitting.
Treatment of coccyx pain
The strongest analgesics are recommended, reaching the administration of Morphine. Sometimes even under this treatment the symptoms do not subside.
The patient’s life is extremely affected, the quality of sleep is low. Radiation therapy is a method that can relieve coccyx pain. It is used in patients with advanced disease. In the long run, however, this method can decrease the body’s resistance and new cancers can appear in the irradiated area.
A healthy lifestyle can prevent many of the common ailments these days. Prevention is the most effective way to fight a disease.
When this type of pain was caused by a crack in osteoporosis, it is absolutely necessary to treat this disease.
First of all, a diet will be followed.
Smoking and alcohol consumption are prohibited, body weight is reduced and sports are recommended as much as possible.
Calcium and vitamin D should be given to women who have reached menopause and are experiencing these pains.
If the pain is from a tumor, it is essential to detect the type of cancer and, depending on the stage of the disease, appropriate treatment will be recommended.