A risk factor is something that increases the chances of having back pain. Having more risk factors means that you have a higher chance of having this type of pain. A unique problem for many reasons, low back pain can be treated in so many ways and by so many specialists.
Based on several studies published by the National Institutes of Health, we can say that 80% of adults are more likely to suffer from back pain throughout life. Most people resort to medications, massage devices or all kinds of treatments to get rid of back pain. It is very important to know the factors that can put us in the situation of suffering from these back pain.
CONTENT:
- Age
- Smoking
- Pregnancy
- Job-related risks
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity
- Mental illness
- Education
- Incorrect and sudden back movements
- Genetics
In the following we will present the most important and common risk factors for back pain:
1. Age
Older people are more at risk. Most patients experience lower back pain as they age. With age, osteoporosis can develop, and if it’s left untreated can lead to fractures. Also, chances of development spinal stenosis increases with age due to lost of cushioning and reduced muscle elasticity in the vertebrae.
While older adults may have pain related to any of the conditions that affect younger adults, people over the age of 60 are more susceptible to pain related to degeneration of the spine. Two of the most common causes of low back pain in older adults include osteoarthritis and spinal stenosis.
Joint osteoarthritis, also called degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis of the spine, is a degenerative condition that develops over time. The pain is caused by damage to the cartilage between the articular facets of the spine. At first, the symptoms may be intermittent, but later they may develop into more stable pain in the lower back and eventually cause sciatica, in addition to low back pain.
As a general rule, the possibility of a compression fracture after any sudden onset of back pain should be considered in adults over 50 years of age, especially in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, and in men or women after administration of long-term corticosteroid. In a person with osteoporosis, even a small amount of force applied to the spine, such as sneezing, can cause a compression fracture.
2. Smoking
People who smoke are more prone to moderate pain than those who do not smoke. Studies have found that people who smoke are more prone to lumbar spondylosis. Scientists are still researching the link between smoking and low back pain to find out more.
3. Pregnancy
The woman’s back is heavily stressed because she carries extra weight during the 9 months of pregnancy. During the pregnancy, the increased weight that the women needs to carry, can cause lower back injuries. The back pain doesn’t dissapears after childbirth.
As the uterus expands, it changes its center of gravity and also stretches (and weakens) the abdominal muscles, affects your posture and puts pressure on your back. It can also cause back pain if you press on a nerve. In addition, the extra weight carried means more work for the muscles and increased stress on the joints, which is why the back may feel more pain at the end of the day.
At the same time, hormonal changes during pregnancy weaken the joints and relax the ligaments that attach the pelvic bones to the spine. This can make you feel less stable and experience pain when you walk, sit, sit for a long time, get up from your chair or get out of the tub, lie down in bed or try to lift something.
More than two-thirds of pregnant women have back pain, especially posterior pelvic pain and middle pain. You may have back pain at the beginning of the pregnancy, but it usually occurs during the second half of the pregnancy and may get worse as the pregnancy progresses. After birth, the pain usually goes away in a few months, although it may persist.
Posterior pelvic pain is felt in the back of the pelvis. It is the most common type of lower back pain during pregnancy, although some women also have middle back pain. You may feel posterior pelvic pain as deep pain on one or both sides of the buttocks or on the back of the thigh. It can be triggered by walking, climbing stairs, entering and exiting the bathtub, twisting and lifting.
Lumbar pain occurs in the area of the lumbar vertebrae in the lower back, higher on the body than the posterior pelvic pain. It can be felt around the spine, approximately at the waist. You may also have radiating pain in your legs. Sitting or standing for long periods of time aggravates the pain, making it more intense at the end of the day.

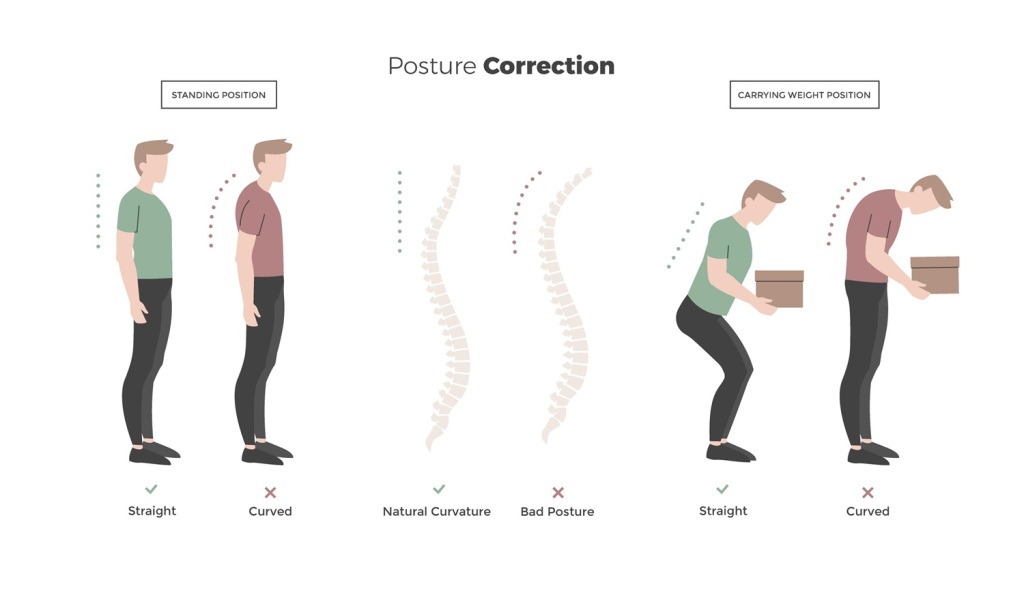
4. Job-related risks
Having a job or other activity that requires long periods of sitting, heavy lifting, bending or twisting, repetitive movements or constant vibrations, such as using a hammer or a certain type of heavy equipment. Any incorrect posture of the spine, maintained for longer, will increase the risk of low back pain. Among the moments when we adopt an incorrect posture are those when we sit at the computer or when we suddenly get out of bed.
5. Sedentary lifestyle
It increases the risk of pain in the lumbar area, as well as their severity. When weak, the abdominal muscles create a lack of support for the spine.
6. Obesity
People at risk are those with overweight and obesity. Extra pounds exert pressure not only on the lumbar area but also on the joints. Overweight / obesity increases the risk of developing low back pain.
Obesity is defined by medical experts as a disease. Overweight (or obesity) is a serious disorder that affects adults and children. Most people know that obesity contributes to the development of coronary heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure and colon cancer.
Obesity can contribute significantly to the symptoms associated with osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis and spondylolisthesis.
The spine is designed to carry body weight and distribute the loads encountered during rest and activity. When we are obese, the spine is forced to assimilate the load, which can lead to structural compromises and damage (eg, injuries, sciatica). One region of the spine that is most vulnerable to the effects of obesity is the lumbar spine. Obesity can aggravate an existing problem in the back and can contribute to the recurrence of this condition.
7. Mental illness
Scientists claim that stress and other emotional factors can create lumbar pain, usually chronic in nature. Stress and other emotional factors play a major role in low back pain, especially in chronic back pain. Many people unconsciously tighten their back muscles when they are under stress.
8. Education
Several studies (Dionne, et al., 2001) have reported that individuals with lower levels of education experience more frequent and longer episodes of debilitating back pain. This connection can find explanation in the nature of work undertaken by less educated individuals, as well as in various other circumstances, including access to health care, smoking and alcohol consumption, unhealthy diet, poor mental health, elevated stress levels, and other factors.
9. Incorrect and sudden back movements
Understanding how movement influences your spine can help you communicate better with your doctor. The better the communication, the faster you will find a treatment that works.
When twisting, the large spinal muscles undergo a slight stretch. The most common reason why movement causes back or neck pain has nothing to do with the bones in the spine. Instead, it is related to the muscles and ligaments that surround the spine.
When you twist your lower back, such as during a golf move or while bending over to unload your shopping bags, you risk exaggerating or breaking any of the large muscles or supporting ligaments around your spine. In response to this damage, the surrounding area will usually become inflamed. This inflammation can lead to a back spasm that will cause middle pain.
The lumbar spine (lower back) is in constant motion and also carries the entire weight of the torso. The movement of the lumbar spine is distributed among five segments of vertebral movement. Each of these segments consists of two joints covered with cartilage and a spinal disc.
The lower discs (L4-L5 and L5-S1) withstand the highest pressure and are therefore most likely to become herniated. A hernia can lead to sciatica pain that radiates to the leg.
Repeated movements, especially for athletes, can lead to vertebral osteoarthritis – or to the mechanical destruction of cartilage between the articulated facets aligned in the back of the spine.
When this happens, the facets of the joints become inflamed, and the progressive degeneration of the joints creates more pain by rubbing. As the back pain progresses, the movement and flexibility of the spine decrease.
Typical symptoms include:
- More stiffness and pain in the lower spine, in the morning and later in the day.
- More stiffness and pain in the sacroiliac joint in the morning and later in the day.
- Decreased pain during the day, as normal movements shake the lubricating fluid of the joints.
- Low back pain, which radiates to the pelvis, buttocks or thighs.
10. Genetics
Inheritance can occur for low back pain caused by disc disease, just like eye color in genetics. People with a close family member such as a parent, a sibling or a child with low back pain are four times more likely to have back pain.
Genes can pass on various types of causal conditions, including physical and psychosomatic expressions:
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Osteomalacia
- Spondylosis
- Degenerative disc disease
- Scoliosis
- Back pain caused by obesity
- Back pain caused by psychological factors