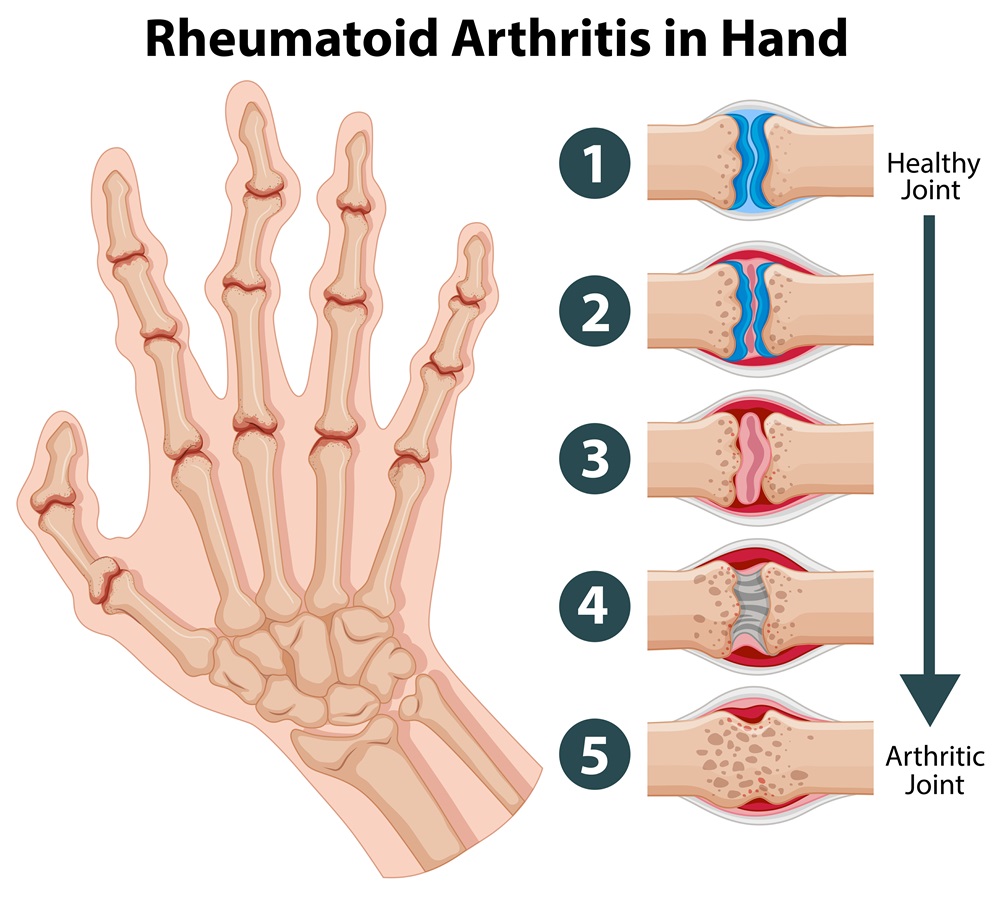
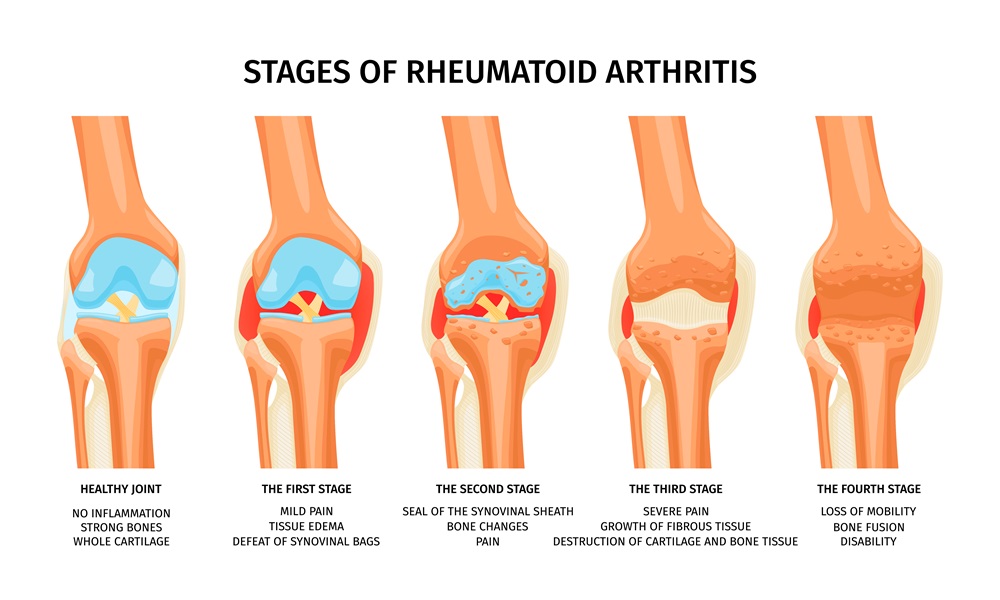
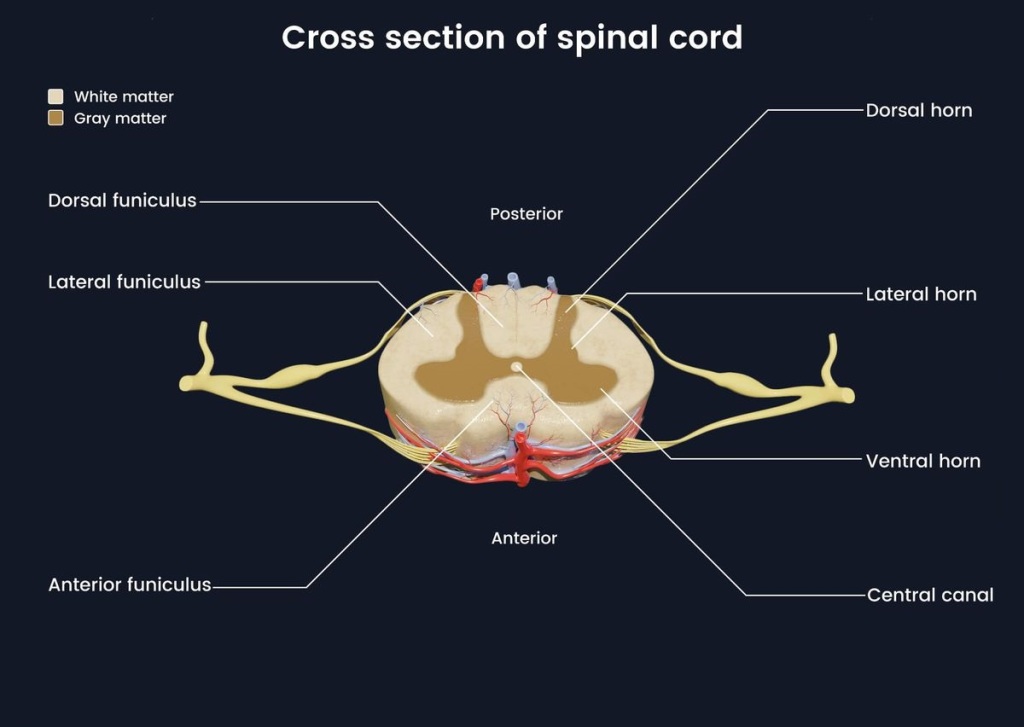
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is an inflammatory disease of the joints that affects children and adolescents. It is an autoimmune disease and symptoms can range from swelling and pain to problems with growth and development.
Parents play a crucial role in managing this condition, and this guide offers answers to common questions they may have.
CONTENT:
- Frequently asked questions for parents
- How can parents help their children?
- Can juvenile arthritis be temporary?
Frequently asked questions for parents
When faced with the diagnosis of a condition such as Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, parents are often faced with a lot of questions and uncertainties. In this segment of our article, we aim to address those frequent questions that arise in the minds of parents when their children are diagnosed with this complex condition.
From the nature of the disease and ways of diagnosis to treatment options and implications for daily life, together we will explore the answers that can bring clarity and understanding to this medical journey.
It is important that parents feel informed and prepared to support their children adequately, and the answers to these essential questions will provide a useful guide in this direction.
-
What is Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)?
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis is a form of arthritis that affects children and adolescents, characterized by inflammation of the joints and sometimes other organs. The exact cause is unknown, and the term “idiopathic” indicates that there is no obvious cause of the disease.
-
What are the symptoms of JIA in children?
Symptoms can vary, but common ones include swelling, persistent joint pain, morning stiffness, muscle weakness, and difficulty performing certain movements. It is important to note any unusual changes in your child’s behavior or activities.
-
How is JIA diagnosed in children?
The diagnosis of JIA often involves close collaboration between medical specialists, including pediatric rheumatologists. Medical examination, physical examinations, and blood tests can be used to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes of the symptoms.
-
What are the treatment options for children with JIA?
Treatment may include anti-inflammatory drugs, physical and occupational therapy, and in some cases, immune-modulating drugs. It is important to discuss the benefits and risks of each treatment option with your medical team.
-
What is involved in the daily management of JIA in the family?
For parents, day-to-day management of JIA may include taking medications regularly, attending physical or occupational therapy sessions, and closely monitoring symptoms. Open and honest communication with the child is also essential.
-
How does AIJ affect children’s school and social life?
JIA can bring additional challenges to children’s school and social life. Parents should work together with teachers and other professionals to ensure an appropriate and supportive learning and socializing environment.
-
What is the long-term outlook for children with JIA?
The long-term outlook varies depending on the severity of the disease. With appropriate treatment and effective management, many children with JIA can lead active and healthy lives. Regular medical monitoring is essential to detect and manage potential complications.
How can parents help their children?
For parents who have children diagnosed with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA), appropriate support and care play a critical role in managing the disease and ensuring the children’s quality of life. Here are some ways parents can help their children in this situation:
1. Education and Information
Understand as much as you can about JIA, treatment and symptom management. The more informed you are, the better informed decisions you will be able to make regarding your child’s health.
2. Open Communication
Establish open communication with your child. Encourage him to share his feelings and thoughts about the illness. An open relationship will make it easier to manage emotions and anxieties.
3. Involvement in Treatment
Actively participate in the treatment plan established by the medical team. Make sure medications are taken as prescribed and that recommended therapies are followed regularly.
4. Promoting Healthy Lifestyle
Encourage a healthy lifestyle with an emphasis on a balanced diet and adequate physical activity. Ask the doctor about the right exercise for your child and create a program that fits his needs.
5. Monitoring Symptoms
Be aware of changes in your child’s symptoms and communicate this information to the doctor. Regular health monitoring will help to adjust the treatment plan according to the evolution of the disease.
6. Psychological Support
Provide emotional and psychological support to your child. It may also be helpful to involve counselors or therapists to provide additional assistance in managing emotions related to the illness.
7. Coordination with the School and Other Professionals
Communicate with teachers and school staff to ensure an appropriate learning environment for your child. Involve specialists, such as physical or occupational therapists, to support the child’s development in all aspects.
8. Encourage Autonomy
Encourage your child to be independent as much as possible. Give him opportunities to develop his skills and assume responsibilities within the limitations imposed by the illness.
9. Managing Family Stress
Every member of the family can be affected by JIA, so it is important to manage family stress. Find support in the community and share experiences with other parents who are going through similar situations.
Essentially, active involvement, emotional support and effective treatment management are the keys to helping children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis lead as normal and healthy lives as possible.
Can juvenile arthritis be temporary?
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) can have different evolutions depending on the specific form of the disease. In most cases, JIA is not a temporary condition and requires long-term management. However, there are also situations where the symptoms may disappear completely or be effectively controlled with treatment, allowing the child to lead an active and healthy life.
There are three main types of JIA, depending on the number of joints affected and other clinical characteristics:
- Oligoarticular JIA (affects less than 5 joints): Some cases of oligoarticular JIA may go into remission, meaning complete disappearance of symptoms. However, it is important to note that in some cases the disease may recur or occur in other joints even after a period of remission.
- Polyarticular JIA (affects more than 5 joints): This form can be persistent and requires long-term management. However, proper treatment can help control symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
- Rheumatoid factor-negative and rheumatoid factor-positive JIA: These forms may have different courses and may require customized treatment strategies.
It is important to emphasize that the individual prognosis of a child with JIA can vary depending on several factors, including the specific form of the disease, the response to treatment, as well as the involvement of other organs in the inflammatory process. Early treatment and effective disease management can significantly improve the quality of life of children affected by Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Always consult the doctor for evaluation and recommendations specific to your child.