Flexion-Distraction techniques are proving to be a staple in the chiropractic arsenal, providing a distinct and effective approach to treating various spinal conditions. The Cox Technique uses a special table and controlled movements to improve the health of patients with conditions like chronic back pain, herniated discs, or spinal stenosis.
In this context, we’ll explore the beneficial effects of Flexion-Distraction Techniques, emphasizing their contribution to spine alignment and effective musculoskeletal management.
CONTENT:
- What are Flexion-Distraction Techniques?
- Benefits of Flexion-Distraction Techniques
- The difference between spinal decompression and flexion distraction
- The mechanism of flexion distraction injury
What are Flexion-Distraction Techniques?
Flexion-Distraction techniques are an advanced and effective method in chiropractic therapy, also known as the Cox Technique. This approach uses a specially designed table and controlled flexion and traction movements to treat various spinal conditions.
The main purpose of Flexion-Distraction techniques is to improve patient health, addressing chronic back pain, herniated discs, and spinal stenosis. Through controlled manipulations adapted to individual needs, this method contributes to the alignment of the spine and the effective management of musculoskeletal conditions.
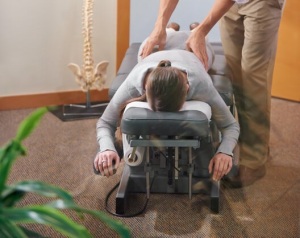
Benefits of Flexion-Distraction Techniques
Flexion-Distraction techniques offer a number of significant benefits in the treatment of spinal conditions and musculoskeletal problems. Here are some of the main advantages of these techniques:
- Correct Alignment of the Vertebral Column: Flexion-Distraction techniques contribute to the correct alignment of the vertebrae, reducing the pressure on the intervertebral discs and restoring the functionality of the spine.
- Muscle and Ligament Relaxation: The controlled flexion and traction movements induced by these techniques have a relaxing effect on muscles and ligaments, reducing muscle tension and improving flexibility.
- Improving Blood Circulation: Flexion-Distraction techniques can stimulate blood circulation in the treated area, helping to deliver essential nutrients to the tissues and promoting the healing process.
- Back Pain Management: These techniques are recognized for their effectiveness in managing chronic back pain, including that caused by herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Adaptability to Various Conditions: Flexion-Distraction techniques can be adapted to a variety of spinal conditions as well as individual patient needs, providing a personalized approach to the treatment process.
- Minimizing Discomfort: These techniques are designed to minimize discomfort and create a more pleasant therapeutic experience for patients without involving invasive procedures or drugs.
- Support in Post-Surgical Recovery: Flexion-Distraction techniques can be beneficial in the post-surgical recovery process, helping to restore functionality and stability to the spine after surgery.
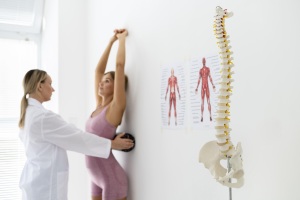
The difference between spinal decompression and flexion distraction
Chiropractic therapy uses spinal decompression and flexion distraction as distinct techniques, each with unique purposes and methods.
Decompression of the spine:
- Purpose: The main purpose of spinal decompression is to reduce pressure on discs and nerves by creating more space between vertebrae.
- Modality: This technique uses specialized devices, like decompression tables, applying controlled and directed traction to the spine. This reduces compression, allowing fluids and nutrients to enter the intervertebral disc, aiding the healing process.

Flexion-Distraction:
- Purpose: Flexion-Distraction Techniques aim to enhance spine alignment and functionality with controlled flexion and traction movements.
- Modality: During Flexion-Distraction, the patient sits on a specialized table, allowing the therapist to perform targeted flexion and traction movements.
The Cox Technique can address various spinal conditions, including herniated discs and spinal stenosis.
In conclusion, decompression reduces disc pressure, while flexion relaxation emphasizes spine alignment and functionality through controlled movements. Moreover, to find the best approach for a spine problem, consult with a chiropractor or spine health specialist.
The mechanism of flexion distraction injury
The Flexion-Distraction technique in chiropractic therapy is a therapeutic approach for spinal conditions. Moreover, it is not an induced injury. This technique uses controlled flexion and traction movements to treat conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and other spine issues.
The therapeutic mechanism of flexion fun includes:
- Creating an intervertebral space: The Flexion-Distraction Technique involves the use of a special table that allows flexion and traction movements. Furthermore, these controlled movements aim to create space between the vertebrae, thereby reducing pressure on the intervertebral discs.
- Opening the nerve channels: Applying flexion and traction opens nerve channels for spinal nerves. Additionally, this aspect can help reduce nerve compression and work on them.
- Improving blood circulation: Controlled movements stimulate blood circulation, delivering essential oxygen and nutrients to affected tissues. This process can support healing and recovery.
Highlight that Flexion-Distraction therapy is safe and non-invasive when administered by trained chiropractors or therapists. This method is used to relieve pain and ensure the functionality of the spine without causing injury. Consult a healthcare professional before starting chiropractic therapy to assess its appropriateness for your situation.


