There are different types of back pain that can affect any region of the back, from the cervical area, at the base of the skull, to the lower back (lumbar) and the sacral area, near the coccyx. Back pain is one of the most common reasons why people go to the doctor or take days off.
Statistically, all people face, sooner or later, back pain. These types of back pain are not a condition, but a symptom that can occur singly or with other manifestations of a disease.
Back pain has a variety of causes, from adopting an incorrect posture to muscle strains or the existence of an internal organ condition. The causes of back pain depend on the type of pain and the area in which it occurs.
Also, it’s good to know that there are a few types of back pain.
CONTENT:
- Back pain in the cervical area
- Back pain in the coccyx area
- Back pain in the chest area
- Low back pain
Back pain in the cervical area
Back pain in the cervical area (neck) can be caused by:
- Dislocations and sprains due to overload;
- Repetitive neck activities;
- An incorrect posture in the chair or during sleep;
- Disc herniation;
- Osteoporosis;
- Migraine;
- Spinal stenosis;
- Fibromyalgia;
- Congenital anomalies of the vertebrae or bones;
- Blows or traumas in the neck area.
Also, neck pain can have serious causes (which can affect quality of life), such as meningitis, heart attack, spine tumors or multiple myeloma (bone marrow plasma cell cancer).
Cervical pain manifests itself in the form of discomfort between the base of the skull and the upper part of the shoulders. The pain may spread to the upper back and arms. Head and neck mobility may be affected and migraines may occur. If the pain occurred as a result of compression of the spinal nerve roots, symptoms such as:
- Numbness;
- Weakness in arms or hands;
- Tingling;
- Burning sensation in arms or hands;
- Sensation of numbness or weakness of the legs;
- Rarely, loss of control over the bladder and intestine.
Back pain in the coccyx area
Back pain in the coccyx area is caused by:
- Pregnancy – birth is the most common cause of pain in the sacral area. Towards the end of the pregnancy, the coccyx becomes much more flexible. This allows her to withstand the movements required for birth. During childbirth, the muscles and ligaments in this area may become overworked. As a result, pain occurs;
- Existence of a trauma – falling or hitting the area during a contact sport or activities such as cycling or boating;
- Degeneration of intervertebral discs due to aging;
- An incorrect posture on the seat or while driving – can put pressure on the coccyx and cause pain and discomfort;
- Menopause;
- Spondylitis;
- Obesity;
- Rarely, the presence of a tumor.
Back pain in the coccyx can be dull pain, which, in certain positions, becomes sharp. It manifests itself especially in a sitting position, when standing, after a long time standing, after a cough, during defecation or sexual intercourse. If the pain causes gait disturbances, the doctor is indicated.
Unlike other forms of pain, it is limited to the coccyx and does not radiate to the pelvis or lower limbs.
Back pain in the chest area
Back pain in the chest area can have the following causes:
- Arthritis;
- Inflammation;
- Osteoporosis;
- Muscle stretches;
- Lung disorders;
- Compression fracture of the spine;
- Kidney disease;
- Scoliosis;
- Obesity;
- Kyphosis;
- Incorrect posture while sitting or exercising;
- Scheuermann’s disease – an inflammation of the joints in the spine.
In rare cases, chest pain can be caused by problems with the esophagus, stomach, pancreas or gallbladder.
Back pain in the chest affects the middle of the back. In addition to pain, symptoms such as numbness and tingling, caused by nerve compression, may be felt.
If there is weakness in the legs or loss of control over the bladder, medical consultation is mandatory. Sometimes, a general state of weakness can set in, marked by fever, chills and unusual weight loss.
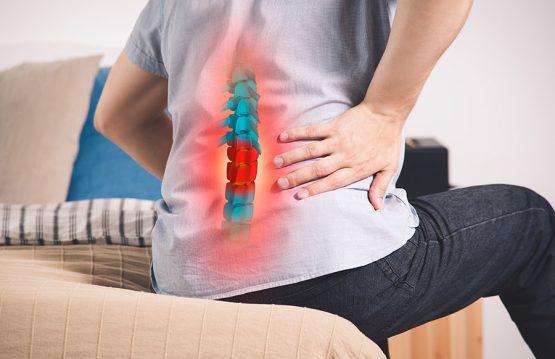
Low back pain
Low back pain can be caused by:
- Muscle stretches;
- Lumbar disc herniation;
- Kidney stones;
- Lumbar osteoarthritis;
- Degenerative disease of the intervertebral disc – especially as a result of aging;
- Lumbar spondylosis;
- Lumbar stenosis;
- A trauma – it can be an accident or a fall.
The back pain in the lower back is felt as a sharp pain, which can be aggravated by standing. It begins intensely in the early hours of the morning, immediately after waking up, and loses intensity during the day or when adopting a comfortable position.
If urinary control is lost or severe abdominal pain or fever occurs, medical consultation is recommended. Sometimes there are muscle spasms, pain in the pelvis or hips and movement becomes limited.
In some situations, the pain is stinging and extends to the lower legs. Sedentary lifestyle also puts pressure on the intervertebral discs and can aggravate back pain. Stretching and walking can help relieve pain, but returning to a sitting position can lead to pain.
Chronic low back pain is usually associated with other symptoms. Most people who have low back pain also experience sleep problems, depression and / or anxiety.
These are the main types of back pain that need to be treated from the beginning of the first common pain.