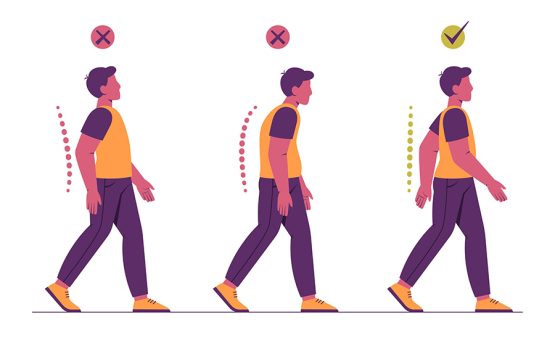
The way you feel the shoes can influence the way you step or the position of the whole body and implicitly of the spine. There are many people who complain of back pain, without imagining that this problem is caused by something as simple as wearing shoes every day.
Without any intention of discrimination, we must recognize that most of the people who choose to wear inappropriate shoes for the sake of trends and fashion are the most women. The offer of footwear is diversified on both sides.
But if in the case of men, apart from preferences and lack of inspiration in choosing the right pair, the risks are much diminished, for women we can find an impressive list of negative aspects, which can bring a lot of suffering, both during a days, as well as long-term.
Choosing the wrong pair of shoes can have the following negative effects:
- the discomfort of always swollen feet
- can cause blisters and painful corns
- the risk of having capillaries and broken blood vessels, even varicose veins
- pain in the fingers, joints, heels, hips, spine
- bone deformation, appearance and accentuation of mounts
- may worsen the health of diabetics
- promotes the appearance of fungal infections and dermatitis of the feet
- can lead to deformity of the pelvic bones and a troubled birth
- change gait
- ensures instability and discomfort throughout the day of activity
- contributes to the risk of injuries, sprains, dislocations, torn ligaments
CONTENT:
High-heeled shoes
High-heeled shoes can be a problem for both women and men. Many women who wear high heels complain of foot pain with bone deformity at this level. Over time, the vicious position leads to pain in the spine.
It is true that heeled shoes give a special elegance to the foot, but over time, this can have repercussions on health.
In other words, it’s not worth following the famous saying that grandma suffers from beauty. Any heel over 5 cm leads to walking with an arched back and slightly bent knees.
This causes the quadriceps muscle to contract excessively due to unnatural gait. All these changes in the muscles and joints of the limbs will eventually affect the spine.
Very low heeled shoes
It is true that heels should be avoided as much as possible. This does not mean that you have to switch to shoes with very low soles.
At the moment it is a real adventure to find the right pair of shoes. Very thin-soled shoes do not provide the necessary support for the foot. In other words, every step will be a chore.
Through the thin sole you will feel every unevenness, so that the gait can change, together with the general posture and the position of the spine.
People who often wear shoes with very thin soles will eventually be affected, in the sense of pelvic and spine pain. They will also have serious problems with the knee joint.
How to choose shoes
Specialists in the field recommend footwear that does not adversely affect the tone and muscles of both the foot and the whole body. The foot is an elastic structure, and the vicious gait caused by poor quality shoes can later lead to deformities, both at this level and at the level of the spine.
There are shoes with orthopedic soles (outer and inner) that offer all the comfort you need, especially for very active people.
The measure should be chosen carefully, because a shoe that tightens can quickly lead to damage to the local vascularity, toe deformation and incorrect gait.
If you have difficulty choosing the right shoe and are already experiencing the devastating effects of uncomfortable footwear (back or leg pain, bone deformities), we recommend that you consider a visit to the podiatrist.
In time, wearing special shoes with the right size and curvature will help you get rid of the unpleasant back pain.
Whether we are talking about the height, the type of sole, the size or the material from which a pair of shoes is made, in choosing the most suitable variant we must take into account a few aspects:
- product quality
- to be the right size
- personal design and model preferences
- the type of activity you do
- the place where you wear them
- always feel comfortable.