Whether it’s the result of sitting at the office all day, constantly using your smartphone, or relaxing on the couch, the improper posture is something we find in people of all ages.
This postural dysfunction represents the unnatural position of the spine, a position in which the natural curves are modified. The long-term result is constant pressure and stress on the joints, muscles and vertebrae.
CONTENT:
- Signs and symptoms of an incorrect position
- What does the wrong position look like?
- Factors contributing to improper posture
- Risks and complications
- Recommendation
Signs and symptoms of an incorrect position
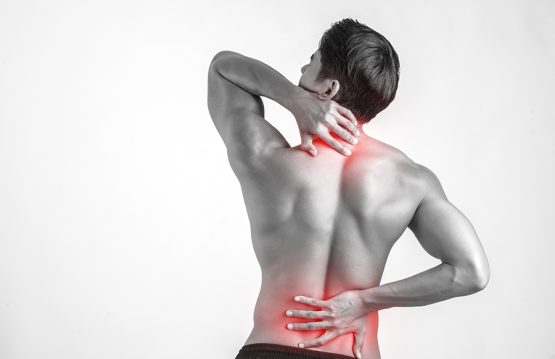
The main symptoms, felt by the person in question daily or once in a while, are painful in nature. Thus, he will feel pain in his upper back (neck) and lower back (lower back), sore throat, pain in his shoulders or upper limbs. Arm pain can often go as far as the wrist and palm. Lower limb pain includes thighs and hips, knees and ankles.
Other symptoms include fatigue and a feeling of “muscle fever”, but also more and more frequent headaches, which we do not usually attribute to incorrect posture.
What does the wrong position look like?
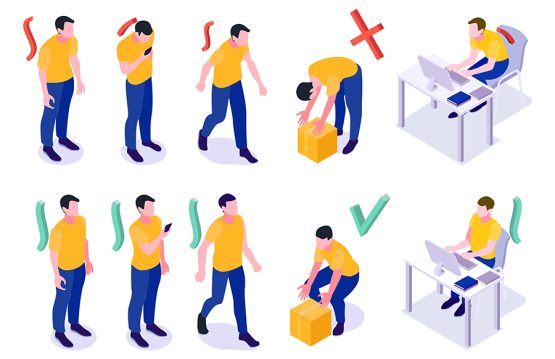
- Incorrect position: Bent over, back bent, shoulders turned forward, neck and head stretched forward, knees bent.
- Incorrect position: Shoulders arched at the back, with the lumbar area much stretched backwards, abdomen protruding in front, shoulders rotated externally, tense.
- Correct position: Back straight and neutral, balanced, forming a straight vertical line from the shoulders to the hips, the neck being aligned with the rest of the body.
Factors contributing to improper posture
- Lack of correct information and awareness of the correct / incorrect position
- Sedentarism
- Some occupational duties
- Muscle stiffness
- Muscle weakness
- Low stability, balance problems
- Stressful lifestyle
- Inadequate working environment
Risks and complications
Although many of us do not realize, maintaining an incorrect position in our daily lives, when we work or relax, can have serious consequences for our health. The worst of these are:
- Permanent bone damage
When the bones are not in their natural position for too long, their abnormal compression and mobilization can occur in the joints. The most serious situation is the vertebral compression, when two neighboring vertebrae overlap unnaturally, hitting each other.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
The nerve fibers that originate at the cervical and thoracic level (upper back) are the same fibers that reach the wrist, where the carpal tunnel is located. Nerves can be affected, compressed, by the unnatural position of the neck and back, leading to this syndrome characterized by pain, tingling, numbness.
- Hypertension
Improper positioning with constant pressure on the joints contributes to high blood pressure, as there are pressure receptors on the neck.
- Urinary incontinence
The incorrect position promotes partial urinary incontinence, defined by urination when the person laughs, coughs or sneezes. When we are not standing, the abdominal pressure increases, pressing on the bladder. The wrong position also weakens the pelvic floor muscles, which can no longer resist the urinary reflex.
- Constipation
This is due to the wrong position when using the toilet, but also to the weakening of the pelvic muscles.
- Heartburn and digestive problems
Heartburn is the burning sensation, retrosternal pain, that characterizes gastroesophageal reflux. Adopting an incorrect position after a meal (lying on your back) can cause reflux accompanied by heartburn, nausea, even vomiting.
The explanation lies in the fact that when we lie on our backs, the gastric acid released for digestion from the stomach will take the wrong direction, reversing, returning to the esophagus.
Recommendation
If you have been lying on your back at least once while reading this article, try the following recommendations to correct your position right now:
- Relax your shoulders, pulling them down and gently back
- Lift your head up, looking straight ahead
- Use your torso muscles: abdominal and pelvic muscles
- Use a special corset to correct posture, if necessary, taking care not to put even more pressure on the torso
- When sitting at the desk, place a small pillow on your lower back; it will help you stay upright
- Change your position every 30-60 minutes
- Do not lie down on the couch immediately after eating