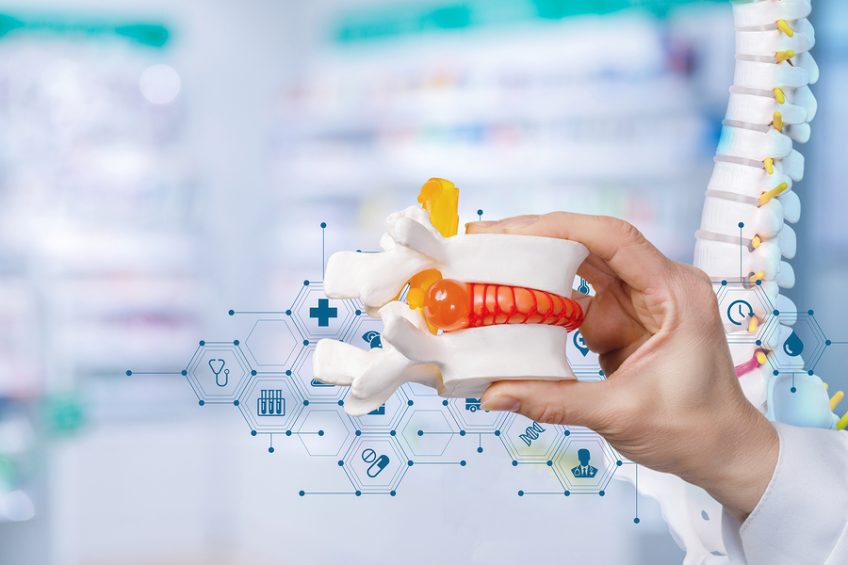
Herniated disc is a condition that occurs when an intervertebral disc is damaged (mainly the fibrous ring – the part located at the periphery of the intervertebral disc), which allows its elastic gelatinous content (pulpal nucleus) to protrude.
A herniated disc due to contact or compression exerted on the nerves or spinal cord can cause pain, numbness and weakness in the hands or feet. Also, not all people who have a herniated disc experience these signs of a herniated disc.
CONTENT:
What are the causes?
Specialists believe that a herniated disc has an important genetic component, especially in patients with lumbar hernia, but most of the risk factors that favor the appearance of a herniated disc are closely related to the fast-forward lifestyle we all know:
- smoking
- predisposition to sedentarism, prolonged sitting
- exaggerated physical exertion after long rest
- lifting weights wrong
- advancing ages
- spinal injuries
These causes are amplified by: obesity, sedentary lifestyle, exposure of the spine to vibrations, birth defects. The people most prone to herniated discs are the elderly, but also those who live in extremes, they do a lot of sports, but neglect the correct posture during exercise or do not exercise at all.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms depend on the position and size of the herniated disc and the presence or absence of nerve compression:
- does not put pressure on a nerve: it may not cause pain
- puts pressure on a nerve: pain, numbness or weakness in the area through which the nerve passes
Symptoms of lumbar disc herniation:
- foot pain (sciatica)
- pain in the lumbar region and / or pain in the gluteal region
- in extremely severe cases there is a loss of sphincter control manifested by urinary incontinence or fecal incontinence
- it usually appears on one leg only
- sudden or graduated onset
- it can be constant or intermittent
- accompanied by numbness, tingling, weakness
- may exacerbate sneezing, coughing, or defecation
- it can get worse due to sitting, prolonged bipedal position or twists
- improves during walking, lying down or other positions that relax the spine and reduce the pressure on the herniated disc
What is the treatment?
Fortunately, doctors rarely recommend surgery for a herniated disc. Detected in time, the condition can be cured by administering drugs and various methods of therapy.
A. Physical therapy
A personalized exercise program will be followed by the patient, and the results will be closely monitored by the doctor. Also, the program aims to reduce the pressure that the herniated disc exerts on the nerve.
Exercise helps the patient to tone the back muscles, which can gradually lead to stabilization of the spine and the disappearance of pain.
B. Physiotherapy
If the physiotherapy does not bring the desired results, the patient can be recommended physiotherapy sessions, accompanied by rest periods, but also the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics.
Physiotherapy can be performed by:
- electrotherapy
- hydrotherapy
- balneotherapy
This method is very effective in relieving pain caused by a hernia and relaxing the muscles in the affected area.
C. Alternative treatment methods
There are also many methods considered alternatives that can relieve the pain caused by a herniated disc. These include:
- massage – performed therapeutically, massage soothes pain, improves blood circulation and helps the secretion of synovial fluid (very important for joint restoration);
- chiropractic – alternative therapy through which the joints are corrected manually by chiropractors; the same vertebral decompression is followed as in the case of elongation;
- acupuncture – a component of traditional Chinese medicine, acupuncture can reduce inflammation and relax the muscles in the affected area;
- yoga – the ancient practices of the Indians can relieve back pain through light exercise, breathing exercises and meditation.
Even if these methods do not involve any danger, it is advisable to talk to your doctor to determine if they can bring you any real benefit.
D. Surgical treatment
Even if they are recommended only in more severe cases, there are certain surgeries through which the herniated disc can be cured.
Disectomy involves the surgical removal of the herniated disc. Unfortunately, this method leaves a free space between the vertebrae, which, in the future, can cause other discs to move. Also, an alternative to dysectomy is microdisectomy, which involves removing only parts of the herniated disc.
Following the dysectomy, the patient remains hospitalized for several days, and recovery can take several weeks. A second alternative to this procedure is chemonucleolysis. This is done by injecting an enzyme into the herniated disc, in order to dissolve the nucleus pulposus.