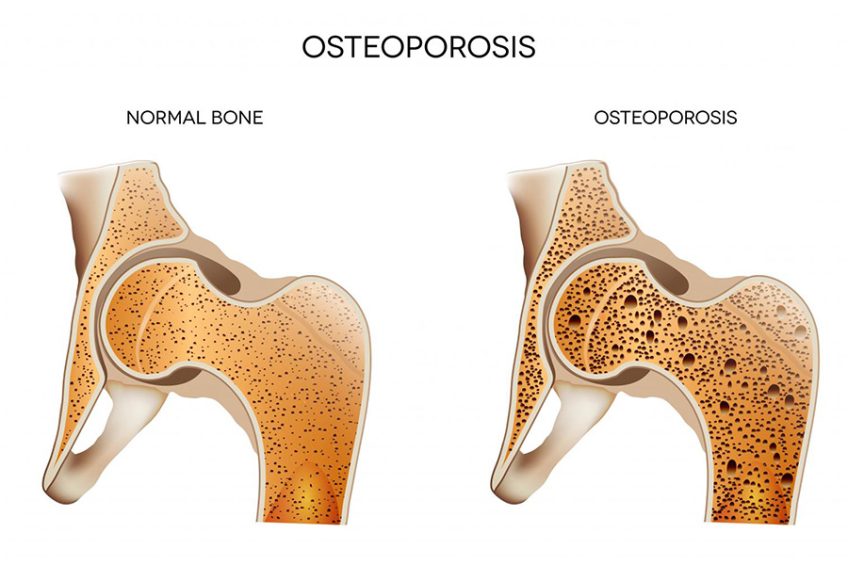
Osteoporosis is a condition of the skeletal system. The bones become fragile, so that even a slight fall or reflexes or daily activities, such as coughing or bending, can cause a fracture. Most often, fractures occur in the wrist, hip or spine.
Osteoporosis can occur in people of any age, but is more common in adults after the age of 50, the most affected being women after menopause. The symptoms of the disease are very subtle, so the disease progresses and causes an increased risk of fractures, during routine activities. The most common fractures occur in the ribs and bones of the wrists, as well as in the spine, but also in the bones of the hip and femur.
Below you can learn more about the symptoms of the disease, the causes and the treatment to be followed to avoid complications and regain, to some extent, worry-free mobility.
CONTENT:
What are the causes of Osteoporosis?
The causes of osteoporosis are only partially known. It is well known that a poor calcium intake can be one of the triggers, but it is far from the only one. Osteoporosis occurs as a result of a combination of factors. Possible causes of osteoporosis include the following:
- some medical conditions, such as hyperthyroidism;
- the use of certain drugs, especially in the class of corticosteroids, as long-term therapy;
- menopause is considered a trigger for osteoporosis, by decreasing the secretion of estrogen and other hormones, the loss of bone mass is more intense, but this singular fact does not necessarily lead to osteoporosis;
- men, in turn, lose bone tissue, also around the age of 50, but at a slower pace than women, and somewhere around the age of 65-70,
- women and men have a declining rate of bone density almost identical;
- parents’ history of osteoporosis increases the risk of developing this disease, which shows that the condition also has a genetic component;
- poor nutrition, combined with physical inactivity, is a factor that aggravates the process of bone demineralization;
- smoking increases the risk of demineralization, because it has an inhibitory effect on cell regeneration, including that of bone tissue, but also because it blocks the mechanism by which estrogen / testosterone mobilizes calcium deposition in bones;
- a low body weight, a low height and a bone structure with small and thin bones favor the disease;
- age is another element that must be taken into account, the risk of this chronic demineralization being real only after 50 years;
- calcium deficiency, combined with a vitamin D deficiency, contributes to the onset of osteoporosis;
- some diseases can lead to bone loss, from genetic diseases (cystic fibrosis) and digestive diseases to multiple myeloma or an aberrant metabolism of calcium and phosphorus;
- alcoholism is another factor that maintains the processes of accelerated bone demineralization.
What are the symptoms of Osteoporosis?
The disease is rarely felt in the early stages. In general, the diagnosis is made only after hip, spine or wrist problems occur. However, there are a number of signs and symptoms that may indicate the onset of bone loss. These include:
- Gum retraction – this problem occurs if the mandible loses bone mass. The dentist can detect this;
- Weakening of the hand – experiments performed on postmenopausal women revealed that the weakening of the hand is associated with a lower degree of bone mineralization. In other words, if the loved one can no longer hold the same hand as before, it is possible to develop osteoporosis;
- Weakening and / or brittle nails – on the one hand, nail health can indicate a problem with the skeletal system. On the other hand, nails can also be affected by factors such as gardening or swimming.
- In addition, if a close relative has osteoporosis, there is a higher risk of developing the disease, in which case an early consultation is recommended, in which it will be possible to detect the disease at an early stage.
When osteoporosis reaches the late stages, more obvious symptoms appear, such as:
- Loss of height – compression of the spine can lead to a loss of height. This is one of the most obvious symptoms of osteoporosis;
- The appearance of fracture – is the most common sign of fragile bones. Fractures can occur as a result of a fall or against the background of minor movements, such as lifting the leg to walk or shopping;
- Back or neck pain – as a result of compression of the vertebral column, nerves are affected and so the pain occurs. This can range from mild discomfort to exhausting pain;
- An incorrect posture.
What is the treatment of Osteoporosis?
Treatment for osteoporosis aims to reduce the risk of fracture. If the disease is discovered early, medications can be given to maintain bone density. Additional forms of treatment will help slow the progression of the disease, reduce disability and partial recovery of mobility. Below you can read about the most used forms of treatment in osteoporosis.
Administration of bisphosphonates
If there is a risk of fracture in the next 10 years, your doctor will recommend bisphosphonate therapy. They slow down bone degradation, reduce pain and prevent abnormal increases in blood calcium levels. Overall, these drugs help in recovery and strengthen bones, improving the quality of life in the long run.
Although they are the most prescribed drugs, bisphosphonates have some side effects. These include abdominal pain, nausea and a burning sensation. To limit these effects, it is advisable to administer the drugs according to the doctor’s instructions.
Hormone therapy
It is especially indicated in cases of early osteoporosis. Women can be given estrogen to maintain bone density. Among the shortcomings of these drugs is a higher risk of blood clots, endometrial cancer and heart disease.
In men, osteoporosis can occur as a result of low testosterone levels. Testosterone replacement therapy can help relieve the symptoms associated with osteoporosis.
Physiotherapy
Usually, the physical therapist works with the patient to develop a personalized exercise plan, which includes weight exercises, such as walking and tennis, and exercises to strengthen muscles and bones, such as weightlifting. .
Adapted exercises will also help correct an inappropriate posture. Improper posture leads to the formation of a rounded area in the upper back. This can increase the risk of spinal fractures.
In addition to specific exercises to relieve the symptoms associated with osteoporosis, physiotherapy can help to perform daily activities that can cause problems for the patient, such as getting out of bed or stool.
Surgery
If the drug treatment is not effective or if the osteoporosis is in an advanced stage, in which the loved one cannot perform light tasks, such as cleaning or walking, the doctor may recommend surgery.
The main intervention indicated in osteoporosis is vertebroplasty. This is a minimally invasive procedure, used to strengthen vertebrae with compression fractures, which occur frequently in patients with osteoporosis. The procedure involves injecting an acrylic compound into the collateral vertebrae to help stabilize the weakened bone. The treatment of each vertebra lasts about an hour and is performed under local anesthesia.
After the intervention, the pain occurs in 70-90% of cases and, in the absence of complications, the patient is released from the hospital on the same day. To reduce pain, your doctor recommends anti-inflammatory drugs.
If there are spinal fractures, cypoplasty is recommended for correction. This is a minimally invasive procedure, recommended to restore the height of the vertebrae and to stabilize weakened bones. It is especially recommended for patients who have had spine fractures in the last 2-4 months.
The intervention consists in making a small incision, through which a balloon catheter is inserted into the vertebra. The balloon is slightly inflated to lift the compressed vertebra, then deflated. The vertebra is injected with a cementitious material, which hardens quickly. The procedure is performed at the hospital, under local anesthesia, and after the intervention, the person can go home. The pain may persist for up to two days, but intense activities, such as lifting relatively heavy objects (eg shopping bags), are not recommended for at least six weeks.
Naturist treatment
Naturist treatment is recommended as a supplement to drug treatment and / or physiotherapy. Applying essential oils on painful areas can help soothe. Also, taking natural supplements can help relieve symptoms. These should only be taken with your doctor’s instructions. Thus, it is recommended:
- Magnesium (500 mg / day) – helps metabolize calcium;
- Calcium (1,000 mg / day) – in the form of calcium citrate, is much more easily absorbed by the body;
- Vitamin D3 (5,000 IU / day) – improves calcium absorption;
- Vitamin K2 (100 mcg / day) – contributes to the formation of the protein involved in bone formation;
- Strontium (680 mg / day) – helps to improve bone density.