Vertebral fractures represent significant medical events, characterized by damage to the bone structures that make up the spine. This region of the body has an essential role in maintaining stability and mobility, and fractures in this area can have serious consequences for the patient’s health. There are various causes that can contribute to these fractures, including trauma, conditions such as osteoporosis, or other pre-existing medical conditions.
Trauma and Causes of Vertebral Fractures
A common factor that can lead to vertebral fractures is trauma, resulting from events such as car accidents, severe falls, or sports accidents. Sudden force applied to the spine can cause fractures of varying degrees of severity.
Osteoporosis and Bone Fragility
Another important cause is osteoporosis, a medical condition characterized by loss of bone density. In osteoporosis, the bones become more fragile and susceptible to fractures. Vertebral fractures in this category can occur from even minor trauma or ordinary pressure.
Other Contributing Medical Conditions
There are other medical conditions, such as bone tumors or spinal infections, that can contribute to fractures. These conditions can weaken the bone structure or exert excessive pressure on them, favoring fractures.
In this context, the article aims to provide a detailed insight into the different types of vertebral fractures, understanding the specific symptoms associated with each type and the available treatment modalities. In addition to this aspect, it is crucial to also examine the potential complications that can occur following vertebral fractures, in order to fully understand the impact on the patient’s health and to guide the recovery process towards an appropriate and effective approach.
CONTENT:
- Compression Vertebral Fractures
- Breakage Fractures
- Flexion fractures
- Settlement Vertebral Fractures
- Fractures in Bulk
Compression Vertebral Fractures
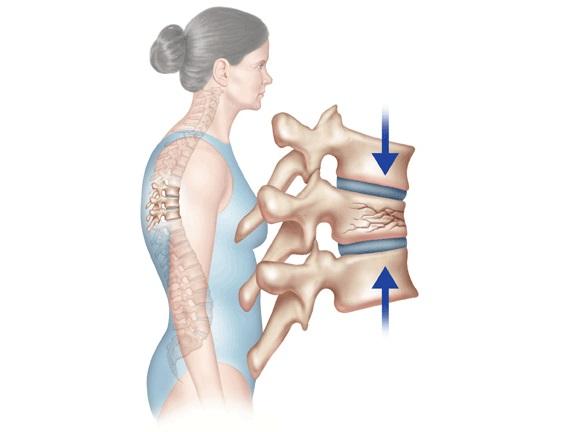
Compression fractures are a specific type of spinal injury that occurs when a vertebra is subjected to excessive pressure, usually from a fall or direct impact. This form of fracture is distinguished by the way it affects the morphology of the respective vertebra.
-
Causes and Triggers
Compression fractures are often the result of a vertical force applied rapidly to the spine. Falls from heights or direct impact, such as in an accident, can create concentrated pressure on one or more vertebrae.
-
Fracture Mechanism
In the case of compression fractures, the vertebra undergoes significant pressure, causing excessive compression of the bone. This process leads to a change in the shape and size of the affected vertebra, usually resulting in a shorter and wider configuration than normal.
-
Characteristic symptoms
Symptoms associated with compression fractures include intense local pain in the affected area. Patients may experience discomfort or pain in the spine, especially around the affected vertebra. Another frequent manifestation is the adoption of a bent or bent posture, reflecting the structural changes of the vertebra.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing compression fractures often involves medical imaging, such as X-rays or CT scans, to accurately assess the extent of the injury. Treatment may vary depending on the severity of the fracture and may include immobilization with braces, pain medication to manage pain, and, in some cases, physical therapy to maintain or restore mobility.
Breakage Fractures
Burst fractures are a distinct type of spinal injury in which the bone is split into two separate parts. This type of fracture can involve significant damage to the bone structure and is often associated with severe trauma, such as car accidents or falls from a height. Exploring the characteristics of these fractures is essential to understanding the consequences and appropriate treatment modalities.
-
Causes and Traumatic Context
Breakage fractures are usually caused by traumatic events such as car accidents, severe falls, or other high-impact incidents. Sudden force applied to the spine can cause the bone to split into two distinct parts, placing considerable stress on the integrity of the bone structure.
-
Sharp Pain and Characteristic Symptoms
Patients with comminuted fractures often experience intense, sharp pain in the affected area. This pain may be localized around the affected vertebra and may radiate to other parts of the spine or body. In addition to pain, patients may experience significant difficulty moving the spine due to the severe injury.
-
Numbness and Weakness in the Lower Limbs
Another common symptom associated with comminuted fractures is numbness or weakness in the lower limbs. This is due to compression or damage to the nerves near the fracture, affecting the proper transmission of nerve signals and muscle strength in that area.
-
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of comminuted fractures often involves the use of advanced imaging techniques such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. Treatment may involve immobilizing the spine with braces, pain medication to control pain, and, in some cases, surgery to restore bone structure.
Flexion fractures
Flexion fractures are injuries to the spine that occur when the spine is subjected to excessive bending or flexion. This type of fracture can have serious consequences on the bone structure and functionality of the spine, and is often associated with events such as a sudden impact or a fall.
-
Causes and Background of the Event
Flexion fractures are often caused by a quick impact or sudden force applied to the spine, causing it to bend excessively. Falls, sports accidents, or any other incident that generates considerable force on the vertical axis of the spine can contribute to this type of fracture.
-
Painful Symptoms and Difficulty in Movement
Localized pain in the affected area of the spine is a primary symptom of flexion fractures. The pain can be intense and radiate to other parts of the body. Patients may also experience significant difficulty moving the spine, which can affect the ability to perform normal daily activities.
-
Affecting Internal Organs
In severe cases, flexion fractures can affect the function of internal organs. The spine protects the spinal cord and plays an essential role in maintaining the integrity of the central nervous system. A severe flexion fracture can compress the spinal cord or damage the nerves that control organ functions, causing additional complications.
-
Diagnosis and Therapeutic Approach
The diagnosis of flexion fractures usually involves the use of medical imaging, such as X-rays or CT scans, to assess the extent and location of the injury. Treatment can vary depending on the severity of the fracture, including immobilizing the spine with braces or casts, pain medication to manage pain, and in some cases, surgery to restore proper alignment of the vertebrae.
-
Rehabilitation and Recovery Process
The recovery process often involves physical therapy aimed at restoring mobility, muscle strength, and normal spinal function. Careful monitoring of potential complications, such as nerve damage or internal organ dysfunction, is crucial for the long-term management of patients.
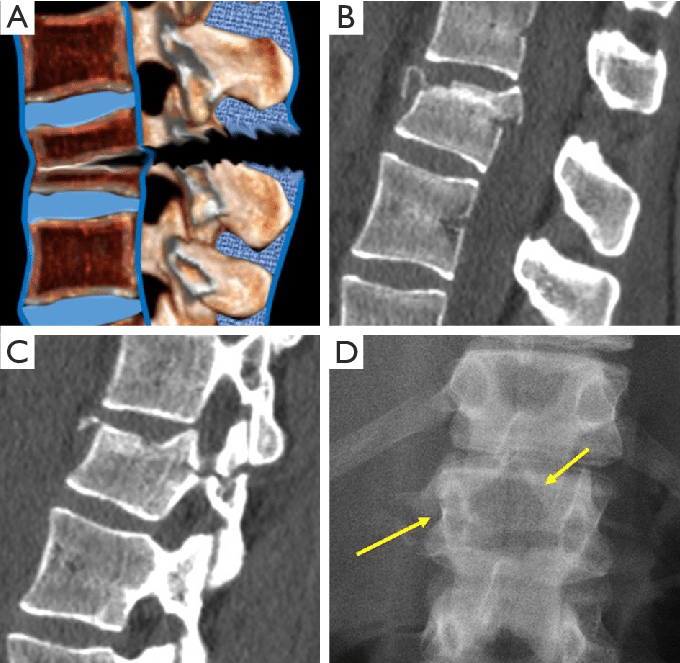
Settlement Vertebral Fractures
Injuries to the spine occur when an axial force is applied directly to it, causing compression fractures. This type of fracture characterizes the sudden compression or settling of the vertebrae, resulting in a significant impact on the structure of the spine. These fractures are common in high-impact accident situations, such as falls from heights or vehicle accidents.
-
Axial Forces and Fracture Mechanism
Axial force applied directly to the axis of the spine causes compression fractures. This type of force can occur at the time of an impact, such as a fall from a height or a vehicular collision. The applied force suddenly compresses and flattens the vertebrae.
-
Causes and Context of Traumatic Events
Traumatic events such as severe falls, car accidents, or falls from a height often associate with dislocation fractures. The violent impact of these events can put extreme pressure on the spine, causing compression fractures.
-
Variation of Symptoms
Symptoms of compression fractures can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Severe pain in the affected area is common, and patients may experience difficulty in moving the spine. In more severe cases, these fractures can affect surrounding structures, causing difficulty breathing or other respiratory problems.
-
Diagnosis and Medical Imaging
The diagnosis of subsidence fractures usually involves the use of advanced imaging techniques such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. These procedures allow doctors to assess the extent and severity of the injury, providing crucial information for treatment planning.
-
Management and Treatment
The treatment of compression fractures may involve immobilizing the spine with the help of corsets or specific devices. Proper pain management and management of complications, such as impaired breathing, are critical aspects of the recovery process.
-
Recovery and Long-Term Monitoring
The recovery process for compression fractures may require physical therapy to restore mobility and muscle strength. Closely monitor patients long-term to detect any potential complications and ensure as complete a recovery as possible.
Fractures in Bulk
Bulk fractures represent a category of spinal injuries characterized by simultaneous damage to several vertebrae. These fractures occur in extreme impact situations, such as plane crashes or falls from great heights, and can have severe consequences on the patient’s health and functionality. Detailed exploration of these injuries is crucial to understanding their complexity and implication in healthcare.
-
Extreme Impact and Bulk Fracture Mechanism
Bulk fractures occur in extreme impact circumstances characterized by strong forces applied to the spine. Airplane crashes, falls from great heights, or other high-energy incidents can cause simultaneous damage to multiple vertebrae.
-
Symptoms Severity of Bulk Fractures
Symptoms associated with bulk fractures are often severe and can vary depending on the severity of the injuries. Intense pain in the affected area is common and can be difficult to control with regular medications. Loss of motor function is a major concern, and patients may experience significant difficulty in performing daily movements.
-
Paralysis and Serious Complications
In extreme cases of bulk fractures, paralysis can occur as a result of damage to the spinal cord. This can affect the functionality of the lower or upper limbs, having a significant impact on the patient’s quality of life. Complications can also include bladder and bowel control problems, often requiring specialist medical attention and intensive rehabilitation.
-
Diagnosis and Prompt Intervention
The diagnosis of bulk fractures often requires the use of advanced imaging techniques, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, to assess the extent and impact of the injuries. Prompt medical intervention is essential to stabilize the spine and minimize the risk of complications.
-
Therapeutic Approach and Rehabilitation
Treatment of bulk fractures can involve complex surgery to realign and fix the affected vertebrae. Immobilization of the spine with specific devices, physical therapy and rehabilitation are essential components of the recovery process, aiming to restore functionality and reduce the risk of long-term complications.